OSINT or Open-source Intelligence is a process of data collection using sources that are open to the public. This can be a wide range of origins – anything from large blogs to specific images and the metadata contained within. Everything posted online discloses some information about the poster and this is what OSINT is looking to find. When you collect this information, the outcome can be extremely dramatic. Data you collect can help to create a dossier with any type of private information about an individual or organisation. Using this dossier, it is possible to mount an attack with devastating consequences.
What OSINT techniques are there?
Open-source intelligence techniques generally fall into 3 categories based on the likely hood of the person collecting the information touching something directly controlled by the target. Therefore, the closer the collector gets to a target the more likely they are to get noticed or detected.
These 3 categories of OSINT techniques are:
Passive – This is when the attacker collects information about a target without touching any services directly controlled or monitored by a target. For example, this can be DNS records, Some social media profiles and WHOIS records. All of these have access logs that are controllable by 3rd parties, making it hard for a target to know that data is vulnerable.
Semi-Passive – Semi-passive data collection is the process of intelligence gathering with processes that seem no different than normal traffic. This could be visiting a service directly controllable by the target but having your traffic blend into that which may be be likely. Some example sources might be an organizations website or a phone call to a service desk.
Active – This is the process of actively interacting with a target’s infrastructure in order to make it disclose information to the attacker. This is the section of OSINT which is most likely to put the information gatherer on the radar. Also, this type of collection can include port scanning, using some transforms in Maltego, as well as going into the building.
The legality of some OSINT techniques can change depending on location and information gathered. Therefore, when you use OSINT, it is extremely important to act within the scope of the engagement and the law.
How can OSINT help?
OSINT is an extremely important part of keeping a business secure. Many companies do not know the information they leak about themselves online and how this can affect their security. Discovering the footprint of the company and finding infrastructure unknown to exist by the company can be a large part of an attack against an organisation. If you worry about your companies online footprint or information disclosure Sencode Cyber Security can help with an OSINT Assessment.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are many different tools used for OSINT, each one of the tools is designed to automate the collection of information from a number of different sources. Some of the most common tools used are:
– Maltego – Maltego is an OSINT automation framework that allows users to collect information from many different sources.
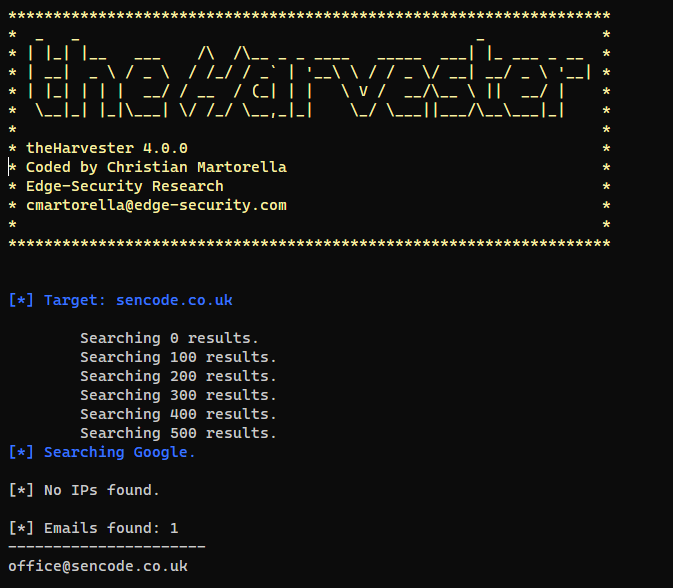
– theHarvester – TheHarvester is used to collect information passively using several different techniques. Designed specifically to collect: emails, names, subdomains, IPs and URLs
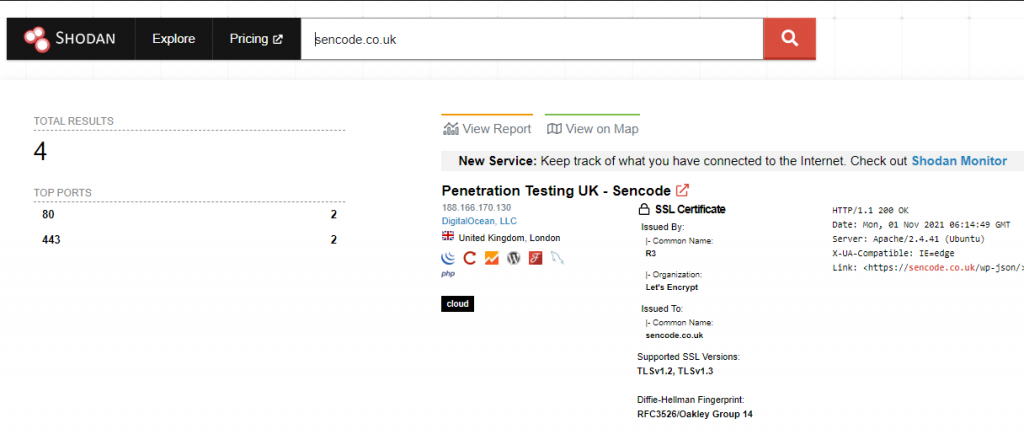
– Shodan – A search engine designed to allow its users to find any internet-connected devices as well as look for known vulnerabilities on them.
The legal status of various Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) techniques can vary significantly based on geographical location and the specific method employed. For example, port scanning, a widely utilised technique, is deemed illegal in numerous European countries. Generally, techniques categorised as passive collection methods are less likely to be illegal. However, it’s crucial to obtain explicit consent before initiating any OSINT activity. This step secures authorisation for data collection and analysis, guaranteeing that all actions are conducted within legal boundaries.