Session management is crucial to ensure that user interactions with web applications are conducted in a secure manner. When a user logs into a system, a session is created that maintains their state and tracks their interactions. This session needs to be unique, secure, and timed correctly to reduce the chances of interception or hijacking by malicious actors.
Good session management will involve generating a unique session identifier (session ID) for each user session, transmitting it securely, and ensuring that the session ID cannot be guessed or reused by an attacker. Insecure session identifiers are a prime target to attackers, who will seek to exploit them in order to compromise a user account.
Session management should also control the lifespan of the session, enforcing session timeouts and ensuring proper user logout to limit the window of opportunity for any potential misuse. The session ID should not disclose any sensitive information and should be protected during transit (e.g., by using secure cookies with the HttpOnly and Secure flags set).
For session management to be effective, all session tokens need to be stored securely on the server and protected against common threats like session hijacking, session fixation, and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). Implementing features such as re-authentication for sensitive actions within a session, automatic timeouts, and transparent user logout helps maintain secure session management protocols.
What is session management in web applications?
Session management is a core component in web application security. It directly deals with maintaining the state and identity of user accounts across multiple requests from hundreds of users, the web server does this concurrently. As HTTP is a stateless protocol, session management techniques are employed to identify and remember users’ actions and settings across different pages. The process of session management involves creating, maintaining and destroying sessions.
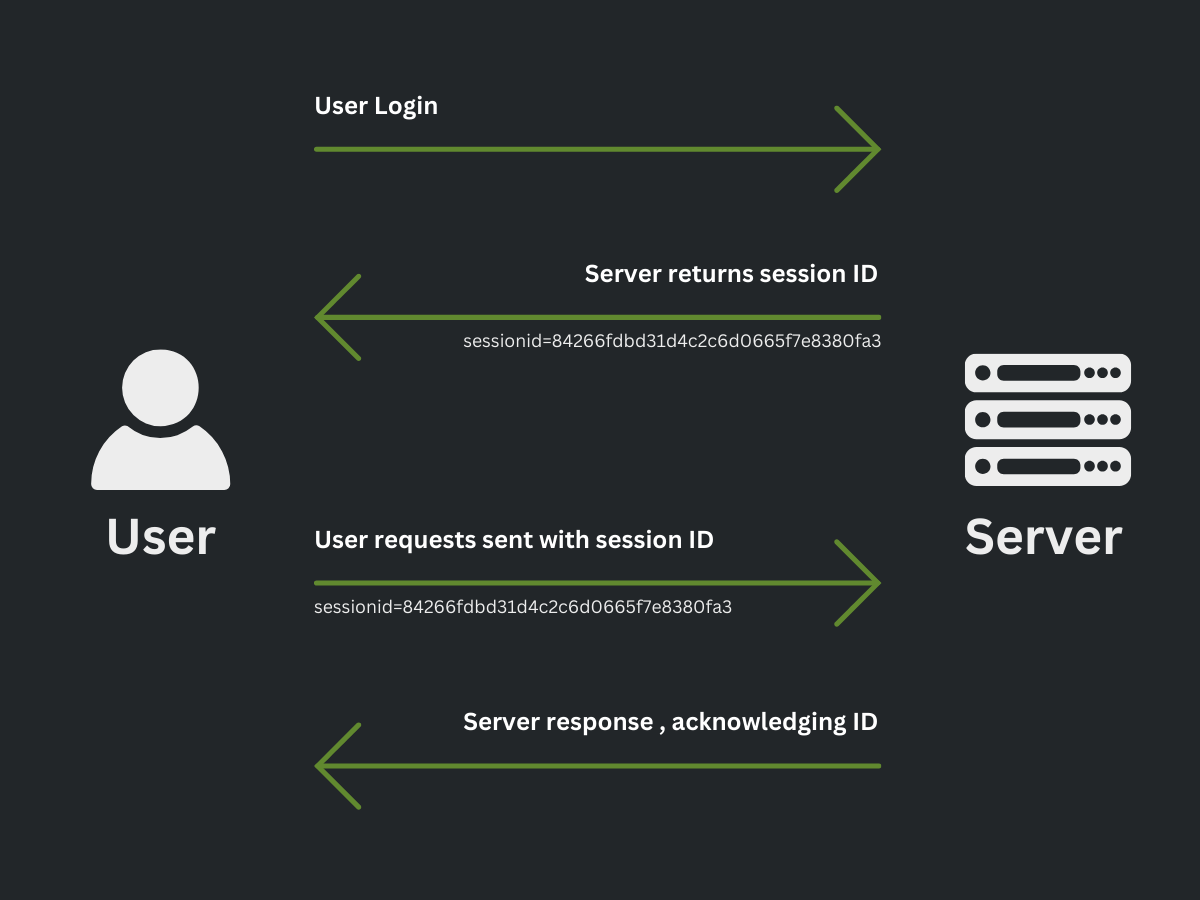
Which session management techniques can reduce security attacks?
There are many techniques web application developers use in order to reduce the effectiveness of security attacks. It is imperative to upkeep good session management practices when developing a web application. Below are some effective techniques to ensure session management is secure and robust.
- Usage of Secure Session Identifiers: All tokens issued by the web application should be generated using a secure, cryptographic random generator to prevent the tokens being guessed by a would be attacker.
- Implement HTTPS: Interactions between the client and server should be secured using HTTPS. This will mitigate the chances of the tokens being intercepted during transit.
- Usage of Cookie Attributes: Tokens issued by the application should be properly configured with the ‘HttpOnly’ and ‘Secure’ cookie attributes. These flags secure the cookies from being accessible via client-side scripts (Such as JavaScript), or transmitted over an insecure connection. It is also advisable to use the ‘SameSite’ attribute where appropriate.
- Session Lifecycle: Tokens should have effective timeouts and expirations policies. This includes both absolute timeouts (E.g. a definitive expiration since login) and inactivity timeouts (E.g. an inactivity timeout, such as 30 minutes of the user making no requests to the server)
- Refresh Session Identifiers: In the event of a change of privilege to a user account, or logout . The session identifier should be refreshed.
- Validated Sessions on every request: Each request should be checked to ensure that is contains a valid session identifier, this is especially important on requests which modify or access any user data.
- Securely Store Session Data: If session data is stored server-side, ensure this is protected from unauthorised access or tampering.
- Limit Session Data Exposure: The amount of sensitive data store in the session should be limited. If possible, keep critical data server-side and only send identifiers or tokens client-side.
- Implement Logout Functionality: Users should always be provided with the ability to logout and terminuate a session. The logout function should terminate the session both client/server-side.
- Monitoring & Logging: Sessions should be monitored in real-time, anomalies or potential breaches should be investigated.
Further guidance and security advice can be found on the Session Management Cheat Sheet provided by OWASP.
Key Characteristics:
- Generation of a unique session ID for each session
- Secure transmission of session IDs
- Handling of session lifecycle (including creation, maintenance, and termination)
- Defense against session-related attacks (e.g., hijacking, fixation)
- Secure storage of session tokens
Examples:
- Real-World Example: Many online banking services use advanced session management techniques. After a user logs in, their session ID is monitored for signs of anomalous behaviour that may indicate a hijacking attempt. The session will automatically expire after a period of inactivity, requiring the user to reauthenticate.
- Hypothetical Scenario: A user logs into a shopping website, and their session ID is transmitted over HTTPS to prevent eavesdroppers from capturing it. The session ID is stored in a secure, HttpOnly cookie, which mitigates the risk of cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks compromising the session.
Related Terms:
- Session Cookie: A piece of data sent from a website and stored on the user’s computer by the user’s web browser while the user is browsing. Cookies can be used to manage sessions.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): An attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they’re currently authenticated, often involving the misuse of session tokens.
- HTTPS: A protocol for secure communication over a computer network which is widely used on the Internet. It encrypts the session data during transmission.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): A type of security vulnerability typically found in web applications that allows attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users, potentially compromising session tokens if not properly managed.
- Session Token: A unique piece of data, often a random string. The token is usually generated by a web-server and sent over to the user’s device.
- Session Hijacking: A type of session attack in which an attacker takes control of a user’s session.
Learn better from a video? Here is a fantastic video explaining Session Management concepts by Secure Code Warrior (Great job)

